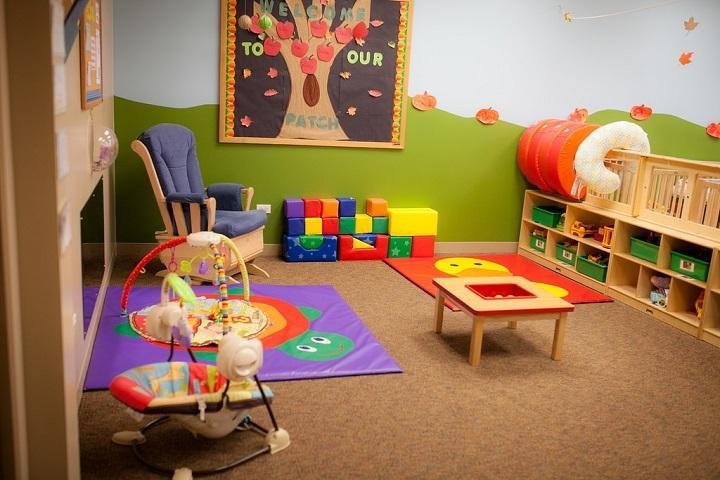
Day care centers provide essential services to families with young children by offering a safe and nurturing environment for children to learn and grow. These centers serve as a valuable resource for working parents who need reliable child care while they are away at work or other commitments.
Additionally, day care centers play a crucial role in early childhood development by providing structured activities and educational opportunities for children. These centers not only ensure the safety and well-being of children but also support their social, emotional, and cognitive development during their formative years.
Importance of Quality Day Care Centers
Quality day care centers, like Day Care Center Avenue U, not only provide a safe and supervised environment for children but also focus on their overall development. These centers offer structured activities that promote learning, socialization, and creativity, which are essential for young children’s growth. By enrolling in a reputable day care center, parents can ensure that their child receives the necessary support and guidance to thrive during their early years.
Supporting Working Families
Day care centers, such as Day Care Center Avenue U, play a crucial role in supporting working families by providing reliable child care services. Working parents can entrust their children to these centers knowing that they are in a safe and nurturing environment while they attend to their work commitments. This support enables parents to pursue their careers and livelihoods without compromising the well-being and development of their children.
Day Care Center Avenue U
Little Scholars at Avenue U
4123 Avenue U, Brooklyn, NY 11234
(929) 810-450
In conclusion, day care centers play a vital role in supporting families by providing a safe and nurturing environment for children to learn and grow. These centers not only ensure the safety and well-being of children but also promote their overall development through structured activities and educational opportunities. Quality day care centers focus on the social, emotional, and cognitive development of children, ensuring that they receive the necessary support and guidance during their formative years. By offering reliable child care services, day care centers support working families, allowing parents to pursue their careers without compromising the well-being of their children. Overall, day care centers are essential resources for families with young children, providing a foundation for learning and growth during the early years of childhood.